3 Ways Self-Evolving Agents Will Reshape the Workforce
Autonomous Process Optimization Through Reinforcement Learning
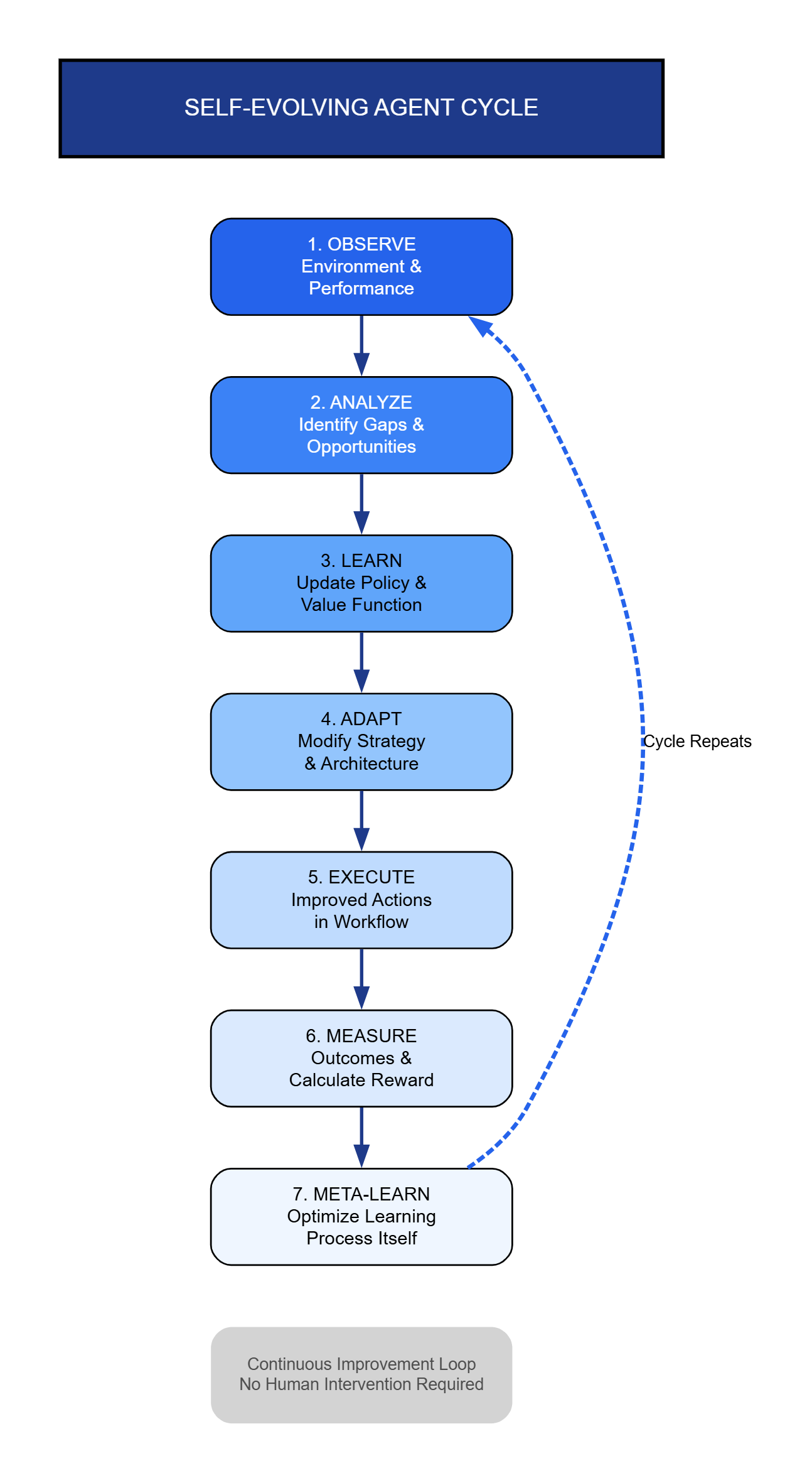
The workforce stands at the precipice of a fundamental transformation. Self-evolving agents autonomous systems that learn, adapt, and improve without human intervention are emerging as the catalysts for this change. These intelligent systems leverage reinforcement learning, neural architecture search, and evolutionary algorithms to continuously refine their capabilities, creating a paradigm shift in how organizations operate.
Understanding Self-Evolving Agent Architecture
Self-evolving agents represent a significant leap beyond traditional AI systems. While conventional machine learning models require retraining and manual updates, these agents implement continuous learning loops that enable autonomous improvement. The architecture comprises three core components: a policy network that determines actions, a value function estimating long-term rewards, and a meta-learning module that optimizes the learning process itself.
Key capabilities:
Continuous learning loops eliminate the need for manual retraining and version updates
Meta-learning modules enable agents to optimize their own learning processes autonomously
Generalization beyond training data through curriculum and transfer learning techniques
The technical foundation relies on techniques like curriculum learning, where agents progressively tackle increasingly complex tasks, and transfer learning, which allows knowledge gained in one domain to accelerate learning in related areas. This creates systems capable of generalizing beyond their initial training data.
import numpy as np
from collections import deque
class SelfEvolvingAgent:
“”“
A self-evolving agent implementing continuous learning
with policy optimization and adaptive reward modeling
“”“
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, learning_rate=0.001):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
# Initialize policy network weights
self.policy_weights = np.random.randn(state_dim, action_dim) * 0.01
self.value_weights = np.random.randn(state_dim, 1) * 0.01
# Experience buffer for continuous learning
self.experience_buffer = deque(maxlen=10000)
self.reward_model = {}
def select_action(self, state):
“”“Select action using current policy with exploration”“”
logits = np.dot(state, self.policy_weights)
probabilities = self.softmax(logits)
action = np.random.choice(self.action_dim, p=probabilities)
return action, probabilities
def update_policy(self, state, action, reward, next_state):
“”“Update policy based on observed outcomes”“”
# Store experience
self.experience_buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state))
# Compute advantage
current_value = np.dot(state, self.value_weights)
next_value = np.dot(next_state, self.value_weights)
advantage = reward + 0.99 * next_value - current_value
# Policy gradient update
gradient = np.outer(state, self.one_hot(action, self.action_dim))
self.policy_weights += self.learning_rate * advantage * gradient
# Value function update
value_error = reward + 0.99 * next_value - current_value
self.value_weights += self.learning_rate * value_error * state.reshape(-1, 1)
def evolve_architecture(self):
“”“Meta-learning: adjust learning parameters based on performance”“”
if len(self.experience_buffer) < 100:
return
recent_rewards = [exp[2] for exp in list(self.experience_buffer)[-100:]]
avg_performance = np.mean(recent_rewards)
# Adaptive learning rate
if avg_performance > 0.7:
self.learning_rate *= 1.05 # Increase exploration
elif avg_performance < 0.3:
self.learning_rate *= 0.95 # Reduce learning rate
def softmax(self, x):
exp_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))
return exp_x / exp_x.sum()
def one_hot(self, idx, size):
vec = np.zeros(size)
vec[idx] = 1
return vec
# Example usage
agent = SelfEvolvingAgent(state_dim=10, action_dim=4)
# Continuous learning loop
for episode in range(1000):
state = np.random.randn(10) # Environment state
action, probs = agent.select_action(state)
# Execute action and observe outcome
reward = np.random.random() # Simulated reward
next_state = np.random.randn(10)
# Self-evolution through continuous learning
agent.update_policy(state, action, reward, next_state)
agent.evolve_architecture()
Dynamic Skill Acquisition and Workforce Augmentation
The first transformative impact manifests through dynamic skill acquisition. Self-evolving agents can identify skill gaps within organizational workflows and autonomously develop capabilities to address them. Rather than requiring developers to program specific functionalities, these systems analyze performance metrics, recognize deficiencies, and implement learning strategies to acquire necessary competencies.
Real-Time Competency Development
Transformation benefits:
Compressed adaptation timelines from months to days or hours when encountering new requirements
Autonomous capability development through exploratory algorithms that understand new contexts
Continuous workforce augmentation that evolves alongside business needs without manual intervention
Organizations traditionally face months-long delays when adapting to new requirements. Self-evolving agents compress this timeline dramatically. When encountering unfamiliar data formats or integration requirements, these systems deploy exploratory algorithms to understand the new context, then adjust their internal representations accordingly. The process happens continuously, creating a workforce augmentation layer that evolves alongside business needs.
Knowledge Graph Integration
How it works:
Dynamic knowledge graphs map relationships between tasks, tools, and outcomes in real-time
Ever-expanding understanding as agents update graphs with new connections during workflow execution
Sophisticated reasoning about task dependencies and optimal strategies without explicit programming
Modern self-evolving agents construct dynamic knowledge graphs that map relationships between tasks, tools, and outcomes. As agents execute workflows, they update these graphs with new connections, creating an ever-expanding understanding of the operational landscape. This enables sophisticated reasoning about task dependencies and optimal execution strategies without explicit programming.
Autonomous Process Optimization Through Reinforcement Learning
The second major transformation occurs through autonomous process optimization. Self-evolving agents apply multi-objective reinforcement learning to simultaneously optimize multiple performance dimensions speed, accuracy, resource consumption, and cost while adapting to changing constraints.
Adaptive Workflow Orchestration
Key differences from traditional automation:
Emergent execution paths based on learned policies rather than rigid, predetermined rules
Dynamic strategy adjustment through real-time observation and policy gradient optimization
Business-metric driven learning that automatically aligns with organizational performance goals
Traditional workflow automation follows rigid, predetermined paths. Self-evolving agents implement adaptive orchestration where execution paths emerge from learned policies rather than fixed rules. The agents observe outcomes, calculate reward signals based on business metrics, and adjust their decision-making strategies through policy gradient methods or Q-learning variants.
Contextual Decision Intelligence
Intelligence capabilities:
Episodic memory systems store detailed records of past situations and outcomes for pattern matching
Contextual retrieval and application of learned patterns to similar current situations
Nuanced decision-making that captures situational factors human-designed rules might miss
Self-evolving agents develop contextual decision intelligence by maintaining episodic memory systems that store detailed records of past situations and outcomes. When facing decisions, agents retrieve similar historical contexts and apply learned patterns, then update their policies based on the current outcome. This creates increasingly sophisticated decision-making that accounts for nuanced situational factors human-designed rules might miss.
Collaborative Intelligence and Human-Agent Teaming
The third transformation emerges through collaborative intelligence frameworks where self-evolving agents and human workers form symbiotic partnerships. These systems implement inverse reinforcement learning to understand human preferences and objectives by observing human behavior, then align their optimization processes with inferred human goals.
Preference Learning Implementation
Human-AI collaboration features:
Inverse reinforcement learning observes human behavior to understand and align with human objectives
Dynamic preference models update continuously based on human feedback and corrections
Weighted decision-making that balances learned policies with human preferences and suggestions
class CollaborativeAgent(SelfEvolvingAgent):
“”“
Extended agent with human preference learning
and collaborative decision-making capabilities
“”“
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):
super().__init__(state_dim, action_dim)
self.human_feedback_history = []
self.preference_model = np.random.randn(state_dim, action_dim) * 0.01
def learn_human_preferences(self, state, agent_action, human_feedback):
“”“
Update preference model based on human corrections
feedback: 1 (approve), 0 (neutral), -1 (correct)
“”“
self.human_feedback_history.append({
‘state’: state,
‘action’: agent_action,
‘feedback’: human_feedback
})
# Update preference model using inverse RL
preference_gradient = np.outer(state, self.one_hot(agent_action, self.action_dim))
self.preference_model += 0.01 * human_feedback * preference_gradient
def collaborative_action_selection(self, state, human_suggestion=None):
“”“
Select action considering both learned policy and human preferences
“”“
# Agent’s policy-based action
agent_logits = np.dot(state, self.policy_weights)
# Human preference-based modification
preference_logits = np.dot(state, self.preference_model)
# Combined decision (weighted)
combined_logits = 0.6 * agent_logits + 0.4 * preference_logits
if human_suggestion is not None:
# Strongly weight human input when provided
combined_logits[human_suggestion] += 2.0
probabilities = self.softmax(combined_logits)
action = np.random.choice(self.action_dim, p=probabilities)
return action, probabilities
def explain_decision(self, state, action):
“”“
Generate human-interpretable explanation for decision
“”“
policy_contribution = np.dot(state, self.policy_weights)[action]
preference_contribution = np.dot(state, self.preference_model)[action]
explanation = {
‘action’: action,
‘policy_confidence’: float(policy_contribution),
‘human_alignment’: float(preference_contribution),
‘reasoning’: f”Selected based on learned patterns (confidence: {policy_contribution:.2f}) “
f”aligned with human preferences (score: {preference_contribution:.2f})”
}
return explanation
Cognitive Load Distribution
Adaptive assistance capabilities:
Real-time cognitive load monitoring through interaction patterns and performance metrics analysis
Dynamic responsibility adjustment when detecting signs of human overload or stress
Adaptive information presentation that reduces complexity based on current human needs
Self-evolving agents actively monitor human cognitive load through interaction patterns and performance metrics. When detecting signs of overload delayed responses, increased error rates, or deviation from typical patterns agents dynamically assume additional responsibilities or modify information presentation to reduce complexity. This creates adaptive assistance that responds to real-time human needs rather than static capability divisions.
Technical Implementation Considerations
Deploying self-evolving agents requires careful attention to several technical factors. Safety constraints must be implemented to prevent harmful exploration during the learning process. Organizations typically establish sandbox environments where agents can experiment freely, coupled with formal verification methods that mathematically prove certain safety properties hold across the agent’s policy space.
Monitoring and Governance Infrastructure
Essential infrastructure components:
Robust monitoring systems track agent behavior, performance metrics, and learning trajectories
Anomaly detection and rollback mechanisms flag unexpected changes and enable quick recovery
Governance frameworks define boundaries balancing autonomous innovation with risk management
Effective deployment demands robust monitoring infrastructure tracking agent behavior, performance metrics, and learning trajectories. Organizations implement anomaly detection systems that flag unexpected behavioral changes, along with rollback mechanisms enabling quick recovery if agents develop undesirable policies. The governance framework defines boundaries within which autonomous evolution occurs, balancing innovation with risk management.
Frequently asked questions
What distinguishes self-evolving agents from traditional AI systems?
Self-evolving agents implement continuous learning mechanisms enabling autonomous improvement without human intervention. Traditional AI systems require manual retraining, feature engineering, and version updates, while self-evolving agents adjust their capabilities dynamically through reinforcement learning, meta-learning, and evolutionary algorithms operating continuously during deployment.
How do organizations ensure self-evolving agents remain aligned with business objectives?
Organizations implement reward shaping techniques that translate business metrics into reward signals guiding agent learning. This includes preference learning through human feedback, constraint specification defining acceptable behavior boundaries, and hierarchical objective structures ensuring high-level goals constrain lower-level optimization. Regular auditing processes verify continued alignment as agents evolve.
What technical infrastructure supports self-evolving agent deployment?
The infrastructure requires distributed computing resources for continuous learning, time-series databases storing behavioral history and performance metrics, version control systems tracking policy evolution, and sandbox environments enabling safe experimentation. Organizations also implement monitoring dashboards visualizing agent learning progress and decision-making patterns.
Can self-evolving agents operate across multiple business domains simultaneously?
Advanced self-evolving agents implement multi-task learning architectures enabling simultaneous operation across domains while sharing learned representations. Transfer learning mechanisms allow knowledge gained in one domain to accelerate learning in others. However, effective deployment requires careful attention to task interference where optimization for one objective might degrade performance on another.
Transform Your Workforce with Self-Evolving Intelligence
The convergence of self-evolving agents and human expertise creates unprecedented opportunities for organizational transformation. These systems move beyond automation toward true augmentation, where artificial intelligence continuously adapts to complement human capabilities.
Ready to explore how self-evolving agents can reshape your workforce? Our team specializes in implementing adaptive AI systems tailored to your specific operational context. We provide comprehensive assessment, architecture design, deployment support, and ongoing optimization to ensure your self-evolving agents deliver measurable business value while maintaining alignment with organizational objectives.