Why Agentic AI is More Than Chatbots : The Evolution of Autonomy
Discover why agentic AI represents a paradigm shift beyond chatbots. Learn how autonomous AI agents are transforming business operations, decision-making, and productivity in 2025.
The artificial intelligence landscape is experiencing a fundamental transformation. While chatbots have dominated conversations about AI for years, a new breed of technology is emerging agentic AI.
Understanding the Core Difference Between Chatbots and Agentic AI
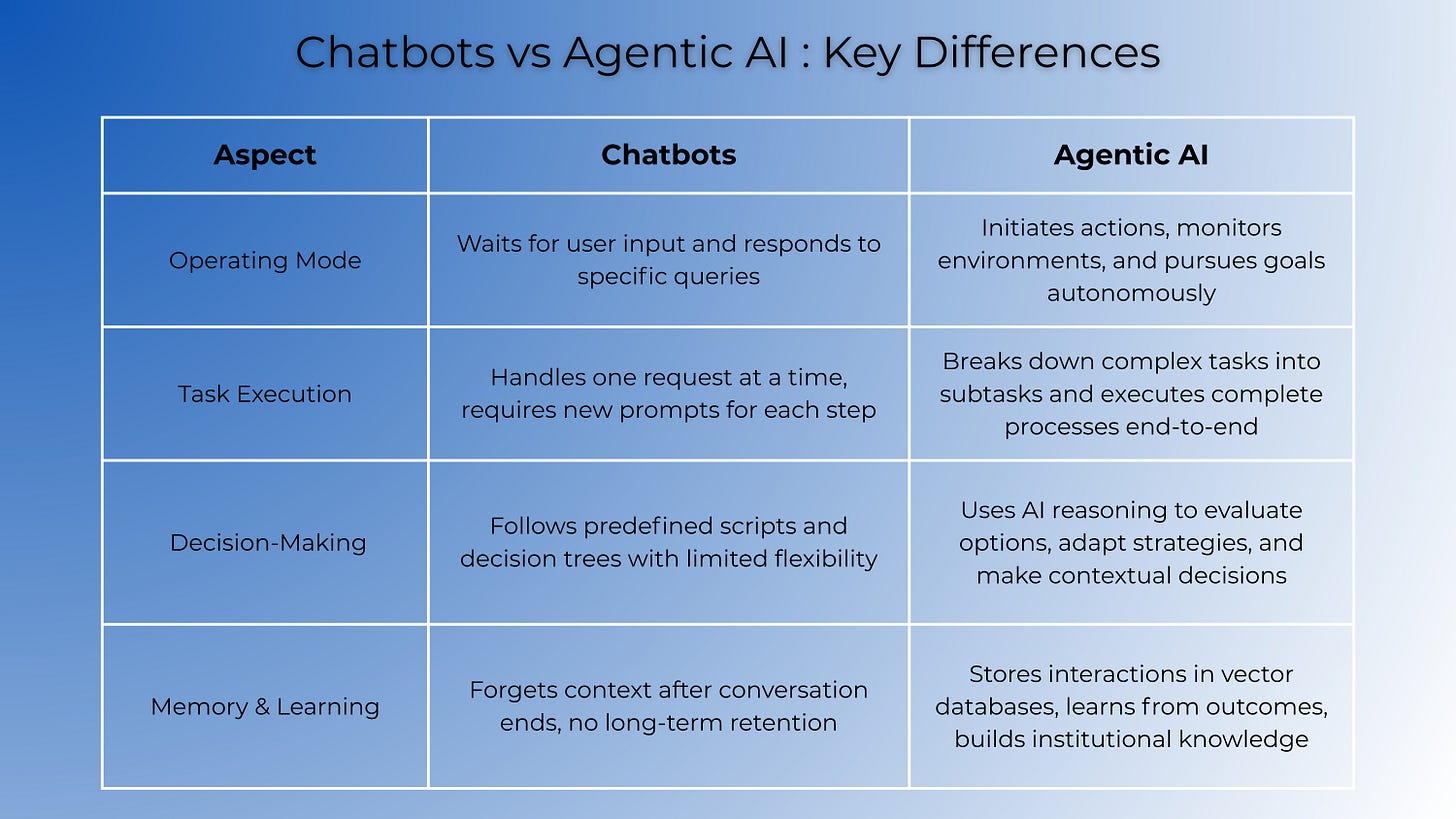
Traditional chatbots operate within strict boundaries. They respond to queries, follow predetermined scripts, and wait for human input before taking any action. Think of them as sophisticated answering machines helpful, but fundamentally reactive.
Agentic AI, however, functions differently. These systems possess the ability to perceive their environment, make independent decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant human supervision. The distinction lies in autonomy, proactivity, and the capacity to learn and adapt from experience.
When you ask a chatbot to schedule a meeting, it might suggest times. An AI agent, on the other hand, can analyze your calendar, check participants’ availability across multiple time zones, book the conference room, send invitations, and reschedule automatically if conflicts arise all without asking for permission at each step.
The Three Pillars of Agent Autonomy
Goal-Oriented Behavior
Unlike chatbots that simply respond, agentic AI systems work toward defined objectives. They understand the desired outcome and chart their own path to achieve it. This means breaking down complex tasks into actionable steps, prioritizing activities, and adjusting strategies when obstacles appear.
Environmental Perception and Learning
Agents continuously gather information from their surroundings, whether that’s data streams, user behavior patterns, or external APIs. They process this information to build an understanding of context and make informed decisions. Machine learning capabilities allow them to improve performance over time based on outcomes.
Independent Decision-Making
Perhaps the most revolutionary aspect is the agent’s ability to make choices without human intervention. Using reasoning capabilities, these systems evaluate options, predict consequences, and select the most appropriate course of action based on their programming and learned experience.
How Agent Systems Process and Execute Tasks
Understanding the technical workflow reveals why agents are so powerful. When you assign a task, here’s what happens under the hood:
Prompt Decomposition: The agent uses chain-of-thought reasoning to break your request into subtasks. Advanced implementations use tree-of-thought or graph-of-thought approaches for complex problems.
Tool Selection: The agent evaluates its available toolset (APIs, functions, databases) and selects appropriate ones. This uses embedding-based similarity matching between the task and tool descriptions.
Execution Loop: The agent enters a ReAct cycle reasoning about the next step, taking action, observing results, and adjusting. This continues until the goal is achieved or predetermined limits are reached.
Error Handling: Unlike brittle scripts, agents use self-correction mechanisms. If an API call fails, the agent can diagnose the issue, modify parameters, try alternative approaches, or escalate to humans.
Memory Consolidation: Successful patterns get stored in vector memory, while failures inform future behavior through reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
Popular frameworks implementing this include LangChain (Python/JS), LlamaIndex for RAG-enhanced agents, CrewAI for role-based agent teams, and Semantic Kernel from Microsoft. Each offers different tradeoffs between flexibility, performance, and ease of deployment.
Real-World Applications Transforming Industries
The practical implications of agentic AI extend far beyond theoretical discussions. Businesses are deploying these systems with measurable results.
In customer service, AI agents don’t just answer questions they identify issues, access multiple systems via REST APIs to gather relevant information, implement solutions through automated workflows, and follow up to ensure resolution. Companies like Intercom and Zendesk now offer agent-based support that resolves 60-80% of tickets without human intervention.
Financial institutions use agentic systems for fraud detection that not only identifies suspicious patterns using anomaly detection algorithms but also takes immediate protective actions like calling account.freeze() or transaction.block() while simultaneously alerting security teams through webhooks.
Building Your First AI Agent: A Technical Primer
For developers ready to experiment, here’s a simplified example using Python and LangChain :
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, Tool
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Define tools the agent can use
tools = [
Tool(name=”Calculator”, func=calculator.run),
Tool(name=”Database Query”, func=db.execute_sql),
Tool(name=”Send Email”, func=email_service.send)
]
# Initialize agent with reasoning capability
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=OpenAI(temperature=0),
agent=”zero-shot-react-description”,
verbose=True
)
# Agent autonomously decides which tools to use
agent.run(”Calculate Q4 revenue from database and email the CFO”)
The agent will independently: query the database for Q4 data, perform calculations, format results, and send the email all without hardcoded logic for each step.
The Future Trajectory of Autonomous AI Systems
As we progress through 2025 and beyond, agentic AI will become increasingly sophisticated. We’re moving toward systems that can handle ambiguity, understand nuanced contexts, and collaborate seamlessly with both humans and other agents.
The next generation will likely exhibit greater emotional intelligence, better understanding of human needs and preferences, and more refined ethical reasoning. Multi-modal capabilities will expand, allowing agents to process and act on visual, audio, and textual information simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes agentic AI different from advanced chatbots like ChatGPT?
While advanced chatbots can engage in sophisticated conversations and provide helpful information, they remain fundamentally reactive they respond to prompts but don’t initiate action or pursue goals independently.
How much does it cost to implement agentic AI?
Costs vary significantly based on use case complexity, required integrations, and scale. Some businesses start with low-code agent platforms costing hundreds per month, while enterprise implementations with custom development may require substantial investment.
What industries benefit most from agentic AI?
Any industry involving complex workflows, high transaction volumes, or time-sensitive decisions can benefit. Early adopters include financial services, healthcare, logistics, customer service operations, and sales organizations.
Subscribe to The Agentic Brief – Your essential newsletter for navigating the autonomous AI landscape. Join many of founders, CTOs, and AI leaders building the future with agentic systems.